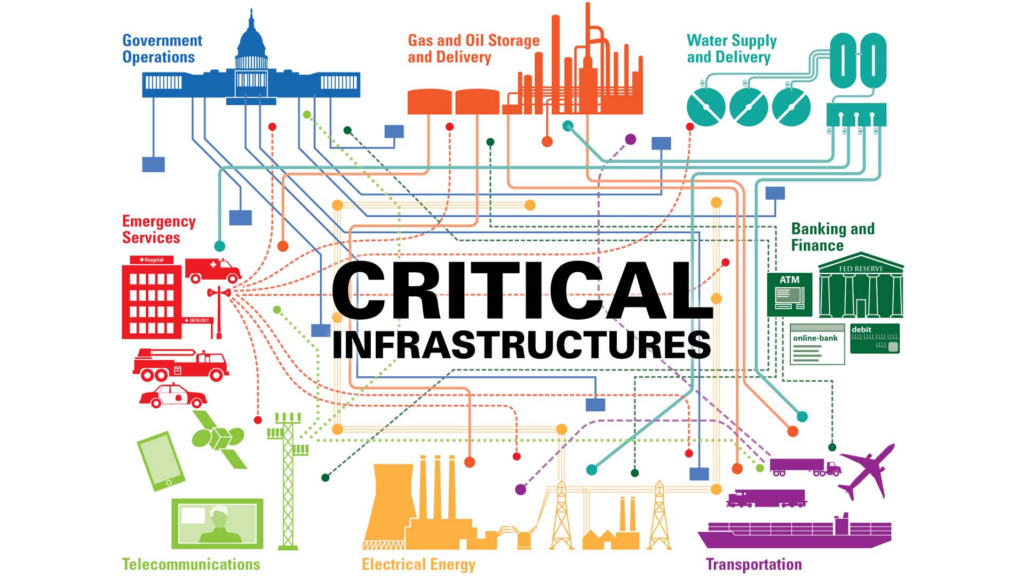
In today’s interconnected world, safeguarding critical infrastructure is vital for national security and societal well-being. Two key frameworks addressing this need are the DHS National Infrastructure Protection Plan (NIPP) in the United States and the European Union’s NIS2 Directive.
Here’s how they compare:
🌎 DHS National Infrastructure Protection Plan (NIPP)
Established by the U.S. Department of Homeland Security (DHS), the NIPP provides a comprehensive framework for managing risks and protecting critical infrastructure across 16 sectors, including energy, water, telecommunications, and healthcare.
The NIPP relies on public-private partnerships, focusing on resilience and post-incident recovery. It uses risk management to identify, assess, and mitigate threats, with tailored plans and strategies for each sector.
Key mechanisms include risk analysis, resilience management, and information-sharing programs to promote close collaboration among various stakeholders.
🌍 EU NIS2 Directive
The NIS2 Directive, set to take effect in 2024, aims to enhance cybersecurity by protecting critical network and information systems across the EU, updating the original NIS Directive from 2016.
NIS2 covers a broad range of sectors, including digital service providers, and mandates harmonized cybersecurity requirements across EU member states, with national authorities and CSIRTs overseeing implementation.
NIS2 enforces strict incident notification, cybersecurity risk management, and compliance reporting, encouraging cooperation and information sharing among member states, with penalties for non-compliance.
🆚 Key Comparisons
▶ Approach:
NIPP focuses on voluntary public-private partnerships for risk management and resilience, whilst NIS2 implements a regulatory approach with harmonized cybersecurity obligations.
▶ Focus:
NIPP addresses both physical and cyber threats, whilst NIS2 primarily targets cybersecurity.
▶ Enforcement:
NIPP uses voluntary partnerships and incentives, while NIS2 imposes legal obligations with penalties for non-compliance.
▶ Collaboration:
NIPP ecourages collaboration between government and private sector, while NIS2 promotes cooperation among EU member states and national authorities.
Both the NIPP and NIS2 aim to protect critical infrastructure but differ in their approaches. The NIPP emphasizes systemic resilience and voluntary cooperation within the U.S., while NIS2 enforces a unified regulatory approach to cybersecurity across the EU. Despite these differences, both frameworks share the common goal of safeguarding vital infrastructures against modern threats.
Gilles CHEVILLON